Next-gen computing inspired by biology
New memristor chips can see patterns over pixels.
 Enlarge
Enlarge
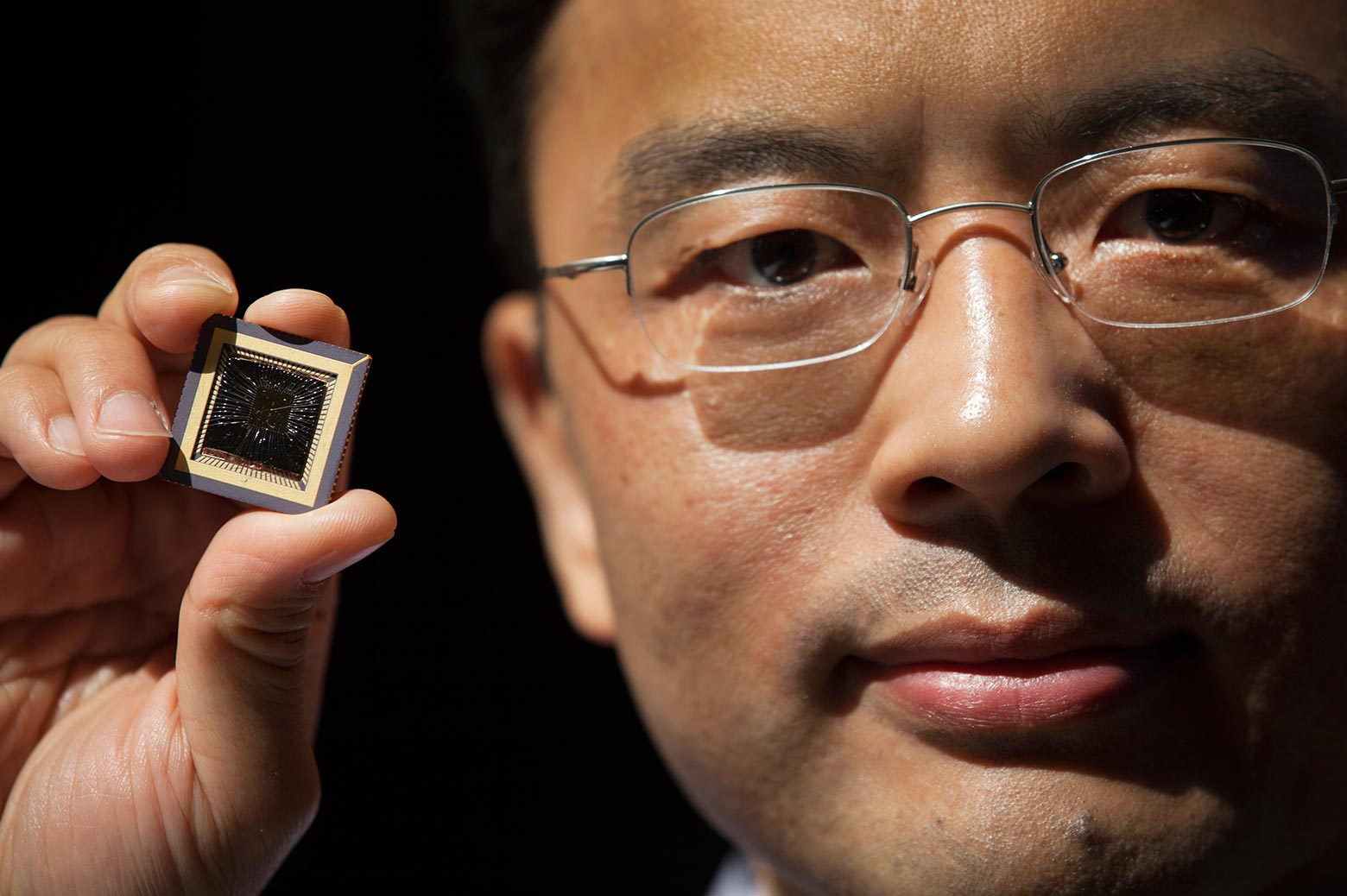
Inspired by how mammals see, a new “memristor” computer circuit prototype at the University of Michigan has the potential to process complex data, such as images and video orders of magnitude faster and with much less power than today’s most advanced systems.
Faster image processing could have big implications for autonomous systems such as self-driving cars, says Wei Lu, U-M professor of electrical engineering and computer science. Lu is lead author of a paper on the work published in the current issue of Nature Nanotechnology.
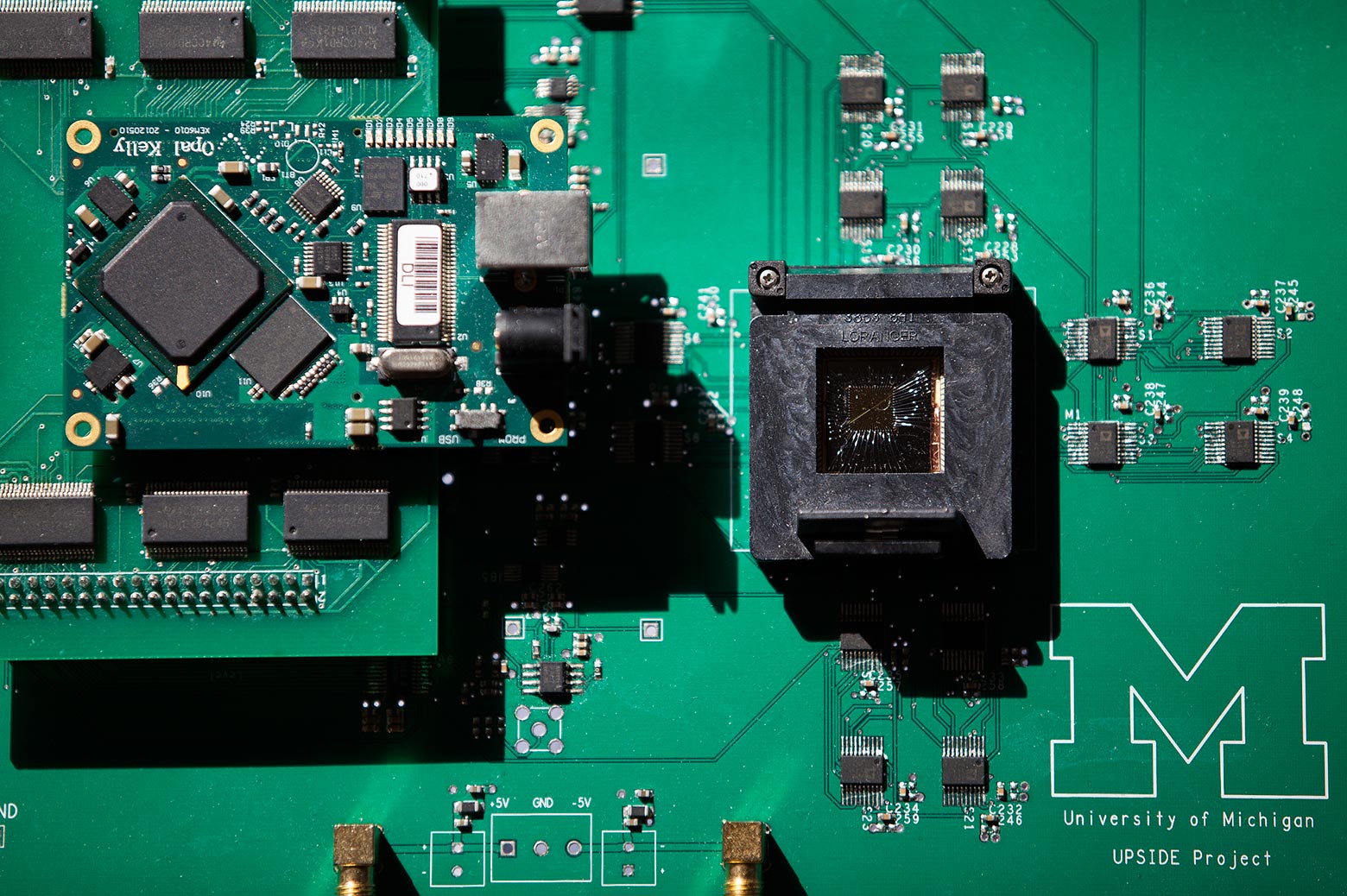
Lu’s next-generation computer components use pattern recognition to shortcut the energy-intensive process conventional systems use to dissect images. In this new work, he and his colleagues demonstrate an algorithm that relies on a technique called “sparse coding” to coax their 32-by-32 array of memristors to efficiently analyze and recreate several photos.
Memristors are electrical resistors with memory—advanced electronic devices that regulate current based on the history of the voltages applied to them. They can store and process data simultaneously, which makes them a lot more efficient than traditional systems. In a conventional computer, logic and memory functions are located at different parts of the circuit.
“The tasks we ask of today’s computers have grown in complexity,” Lu said. “In this ‘big data’ era, computers require costly, constant and slow communications between their processor and memory to retrieve large amounts data. This makes them large, expensive and power-hungry.”
Mammals’ brains generate split-second impressions of what their eyes take in. New #memristor chips are inspired by that process.
Michigan Engineering
But like neural networks in a biological brain, networks of memristors can perform many operations at the same time, without having to move data around. As a result, they could enable new platforms that process a vast number of signals in parallel and are capable of advanced machine learning. Memristors are good candidates for deep neural networks, a branch of machine learning, which trains computers to execute processes without being explicitly programmed to do so.
“We need our next-generation electronics to be able to quickly process complex data in a dynamic environment. You can’t just write a program to do that. Sometimes you don’t even have a pre-defined task,” Lu said. “To make our systems smarter, we need to find ways for them to process a lot of data more efficiently. Our approach to accomplish that is inspired by neuroscience.”
A mammal’s brain is able to generate sweeping, split-second impressions of what the eyes take in. One reason is because they can quickly recognize different arrangements of shapes. Humans do this using only a limited number of neurons that become active, Lu says. Both neuroscientists and computer scientists call the process “sparse coding.”
“When we take a look at a chair we will recognize it because its characteristics correspond to our stored mental picture of a chair,” Lu said. “Although not all chairs are the same and some may differ from a mental prototype that serves as a standard, each chair retains some of the key characteristics necessary for easy recognition. Basically, the object is correctly recognized the moment it is properly classified—when ‘stored’ in the appropriate category in our heads.”
 Enlarge
Enlarge
Similarly, Lu’s electronic system is designed to detect the patterns very efficiently—and to use as few features as possible to describe the original input.
In our brains, different neurons recognize different patterns, Lu says.
“When we see an image, the neurons that recognize it will become more active,” he said. “The neurons will also compete with each other to naturally create an efficient representation. We’re implementing this approach in our electronic system.”
The researchers trained their system to learn a “dictionary” of images. Trained on a set of grayscale image patterns, their memristor network was able to reconstruct images of famous paintings and photos and other test patterns.
If their system can be scaled up, they expect to be able to process and analyze video in real time in a compact system that can be directly integrated with sensors or cameras.
The project is titled “Sparse Adaptive Local Learning for Sensing and Analytics.” Other collaborators are Zhengya Zhang and Michael Flynn of the U-M Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Garrett Kenyon of the Los Alamos National Lab and Christof Teuscher of Portland State University.
The work is part of a $6.9 million Unconventional Processing of Signals for Intelligent Data Exploitation project that aims to build a computer chip based on self-organizing, adaptive neural networks. It is funded by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency.
In the Media
Crossbar pushes resisted RAM into embedded AI
The company, co-founded by Wei Lu, EECS professor, hopes to move artificial intelligence systems into mobile devices.
Memristor image processor uses sparse coding to see
Wei Lu, EECS professor, and his team have designed hardware specifically to run brain-like “sparse coding” algorithms.
Neuromorphic chips offer neural networks that actually work like the brain
Wei Lu, EECS professor, co-authored the study.
New computer chips that ‘see’ data will enable energy-efficient supercomputers
Wei Lu, EECS professor, and his team just published a paper in Nature Nanotechnology describing the new circuit and algorithm, which is based on a principle from neuroscience called sparse coding. Seeker reports.
Neuromorphic chips offer neural networks that actually work like the brain
Wei Lu, EECS professor, co-authored the study.
Memristor research highlights neuromorphic device future
Wei Lu, EECS professor, is working on neuromorphic processor technology. The Next Platform reports.
 MENU
MENU 
